Antarctica, often regarded as the final frontier for scientific exploration, hosts a range of secretive research facilities. These labs, nestled amidst the ice and snow, are hubs of groundbreaking scientific work. From studying ancient ice cores to investigating climate change, these remote research stations offer insights into the mysteries of our planet and beyond.
Ice Core Research Facility
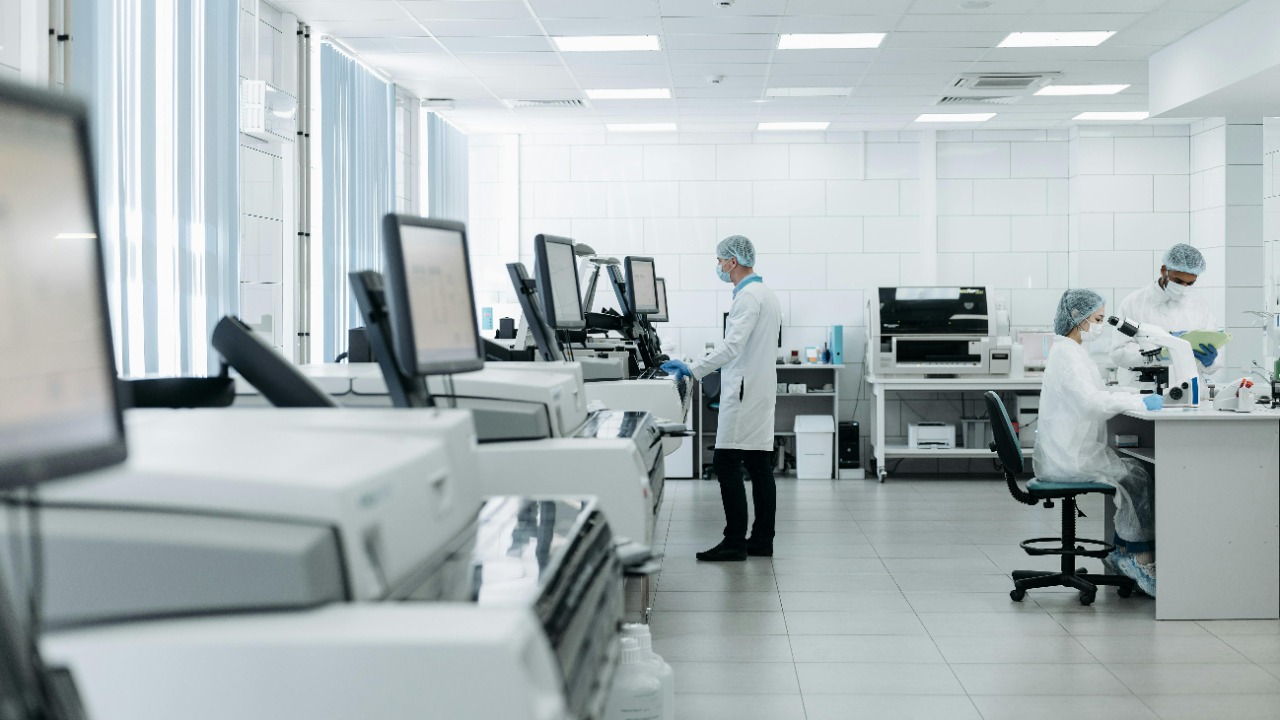

Deep within the frozen expanse of Antarctica, the Ice Core Research Facility is dedicated to unraveling the secrets of Earth’s climate history. By drilling deep into the ice sheets, scientists extract cores that provide a window into past atmospheric conditions. These ice cores contain trapped air bubbles that reveal information about greenhouse gas concentrations over millennia.
Understanding these data is crucial for predicting future climate trends. The facility’s work not only aids in deciphering patterns of climate change but also contributes to global climate models used by researchers worldwide. The ice core data can inform policy decisions and environmental strategies, making this facility a cornerstone of climate science.
Marine Life Observation Station
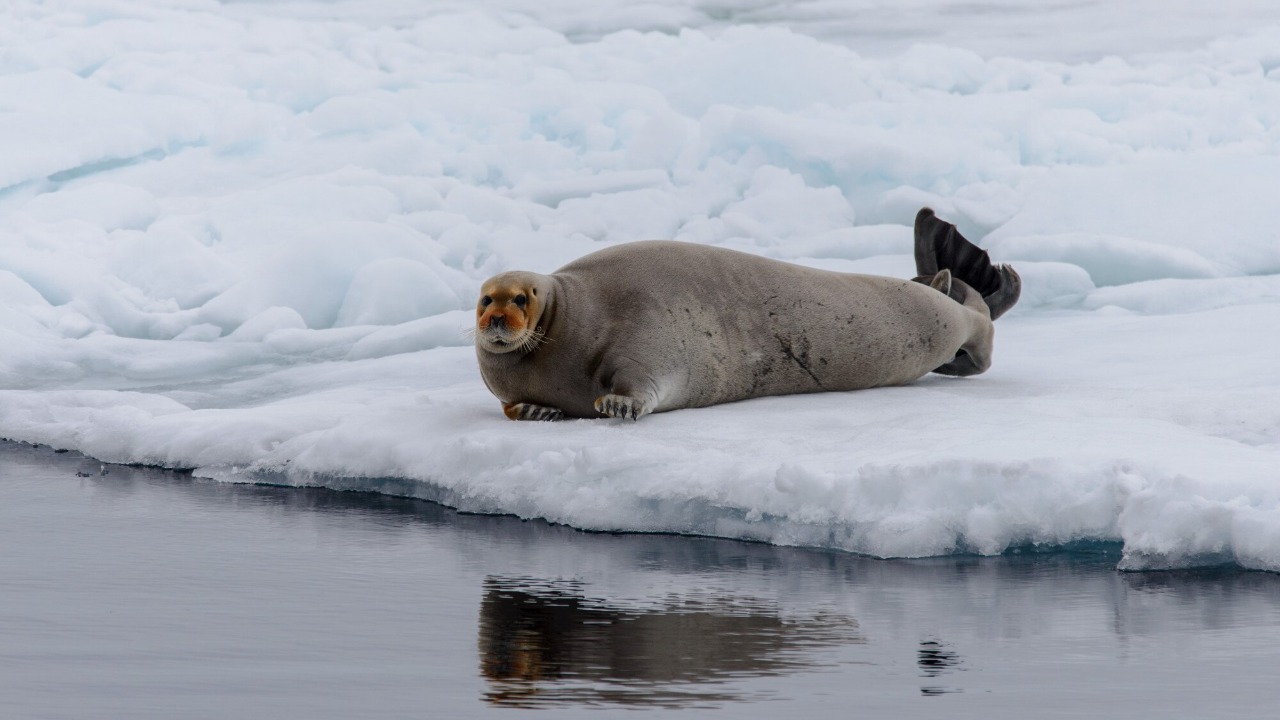

The Marine Life Observation Station is a beacon for biological research in the icy waters surrounding Antarctica. Here, researchers study the unique ecosystems that thrive in extreme conditions, focusing on organisms ranging from microscopic plankton to majestic whales. These studies help scientists understand how marine life adapts to the harsh Antarctic environment.
Insights gained from this station contribute to global knowledge about biodiversity and the impact of climate change on marine ecosystems. By monitoring species population trends, researchers can assess the health of the ocean and predict changes that might affect the planet’s broader ecological balance.
Atmospheric Studies Lab
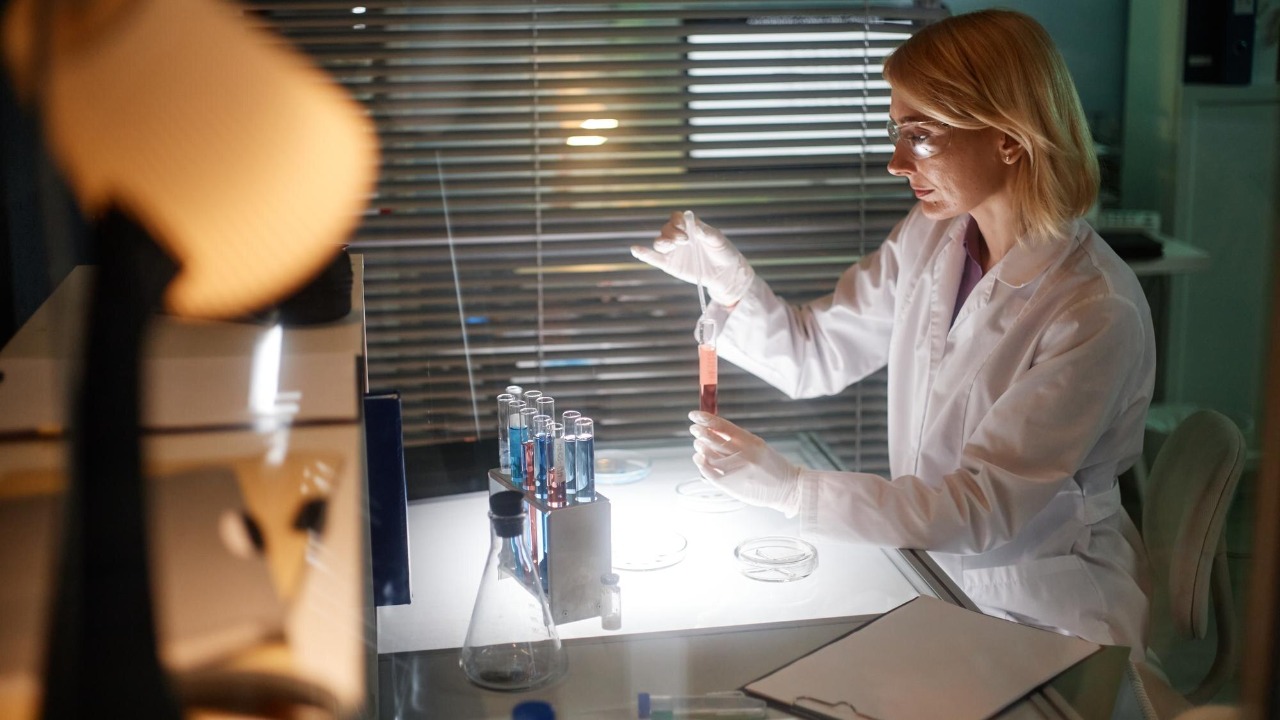

The Atmospheric Studies Lab in Antarctica plays a pivotal role in understanding our planet’s atmospheric dynamics. Positioned far from human influences, this lab provides pristine conditions for studying air composition, ozone levels, and atmospheric particles. It serves as an ideal location for collecting data on global air quality and climate patterns.
The findings from this lab are critical in understanding phenomena such as ozone depletion and their implications for human health and environmental policies. By analyzing long-term atmospheric data, scientists can develop strategies to mitigate adverse effects and improve air quality worldwide.
Glaciology Research Center
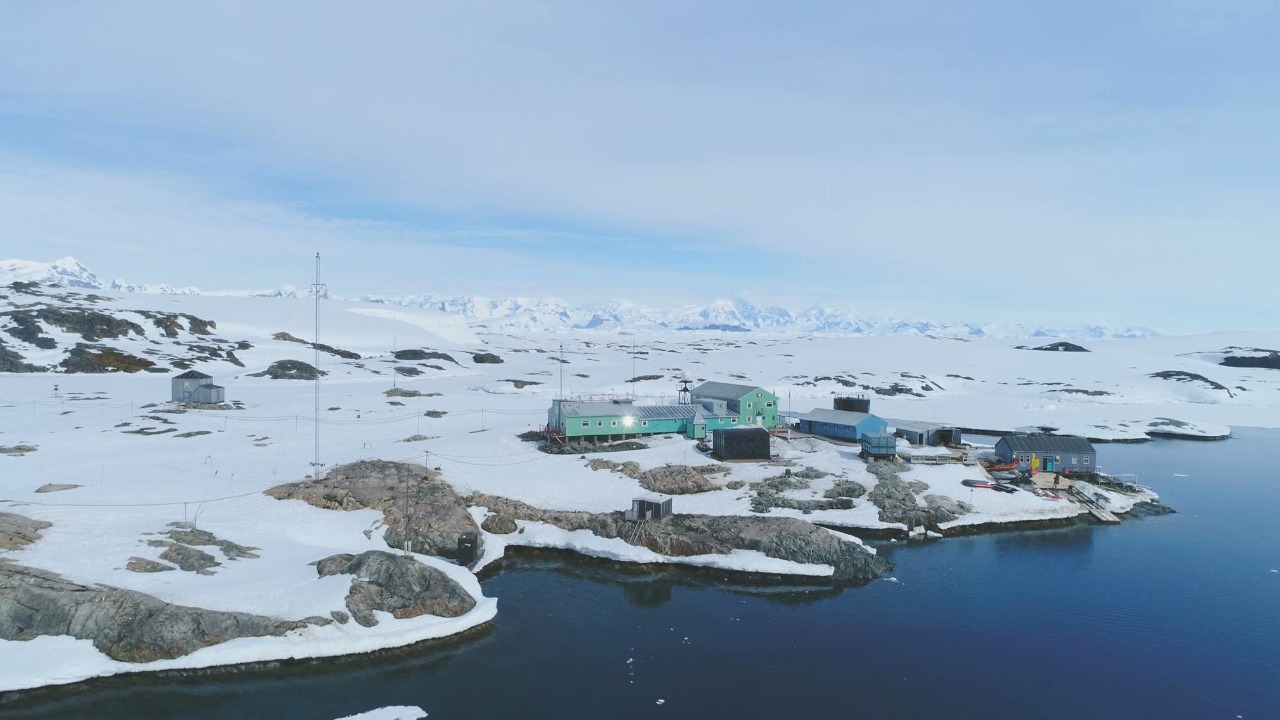

The Glaciology Research Center is at the forefront of studying the dynamics of glaciers and ice sheets. Researchers here focus on understanding how these massive ice formations move and change over time. Their work involves monitoring ice flow patterns, measuring ice thickness, and evaluating the impact of warming temperatures on glacial retreat.
This research is vital for predicting sea-level rise and its potential impacts on coastal communities. By integrating data from satellite imagery and field observations, the center provides valuable insights into the complex interactions between ice and climate, helping to inform global climate policy decisions.
Astrophysics Observation Post
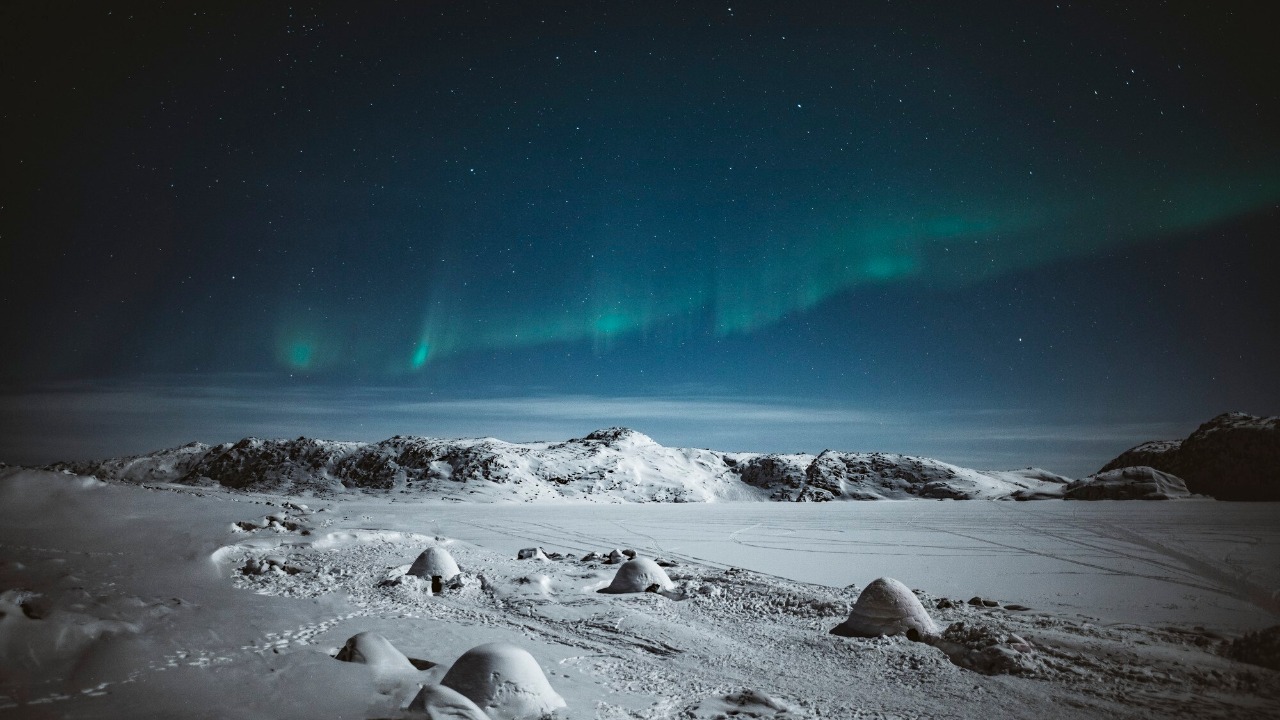

Set against the backdrop of the Antarctic night sky, the Astrophysics Observation Post offers a unique vantage point for studying the universe. The clear, unpolluted skies provide an ideal environment for observing celestial phenomena and conducting research on cosmic radiation, black holes, and distant galaxies.
This station enables scientists to gather data that contribute to our understanding of the universe’s origins and evolution. The isolated location and cutting-edge technology make it possible to conduct experiments that are not feasible elsewhere, allowing researchers to push the boundaries of astrophysical knowledge.
Climate Change Analysis Unit

The Climate Change Analysis Unit is dedicated to understanding the complex processes driving climate change and their effects on the Antarctic environment. Researchers at this facility use advanced models and simulations to predict future climate scenarios and assess their potential impacts on global weather patterns and ecosystems.
By collaborating with international organizations, the unit contributes to the development of mitigation strategies and adaptation plans. Their work is essential for guiding policy decisions aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices worldwide.
Microbial Life Exploration Hub
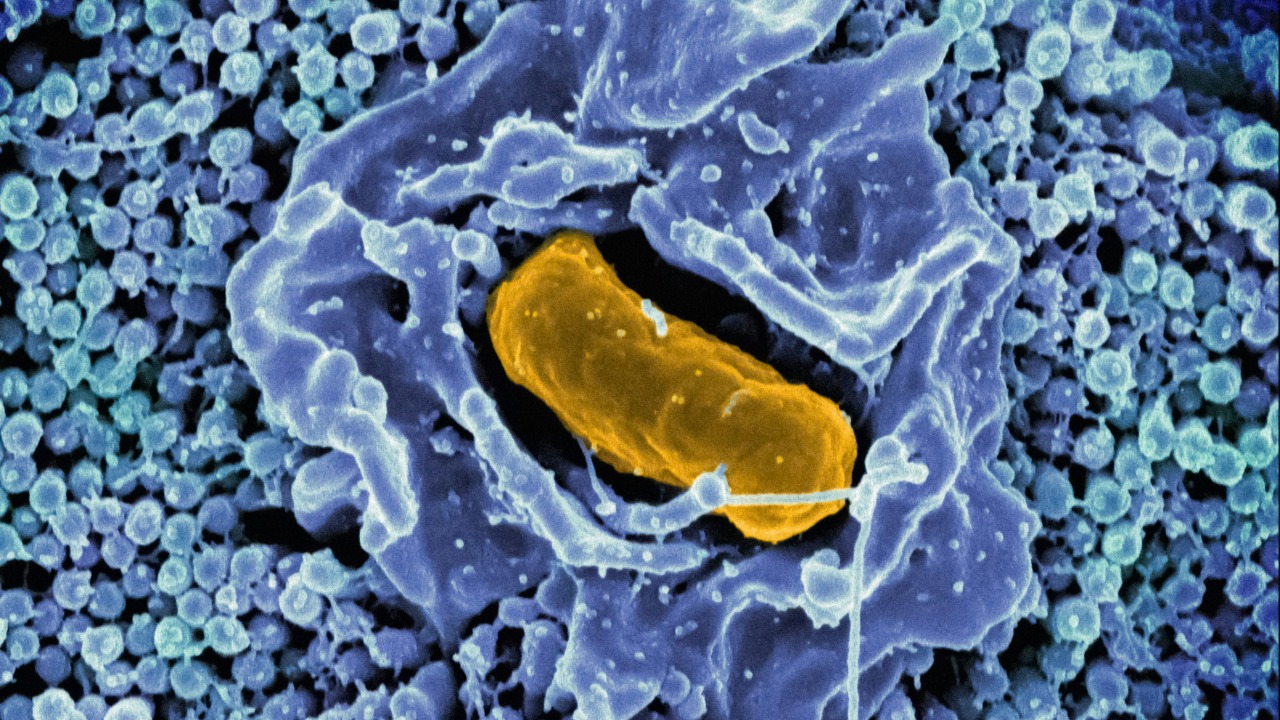
The Microbial Life Exploration Hub delves into the hidden world of extremophiles—microorganisms that thrive in Antarctica’s extreme conditions. These resilient life forms offer insights into the limits of life on Earth and the potential for life on other planets. Researchers study microbial communities in ice, soil, and subglacial lakes to understand their survival mechanisms.
Discoveries made at this hub could revolutionize our understanding of life’s adaptability and resilience. Furthermore, the study of Antarctic microbes may yield biotechnological applications, such as novel enzymes and compounds with industrial or medical uses. For more on the mysteries of Antarctica, explore this fascinating resource.