Our sun, the life-giving star at the center of our solar system, is also a source of powerful forces that could potentially wreak havoc on Earth. While these scenarios might seem like science fiction, the sun’s unpredictable nature means they are worth understanding.
Here are six ways the sun could bring about our end sooner than we think.
Solar Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections
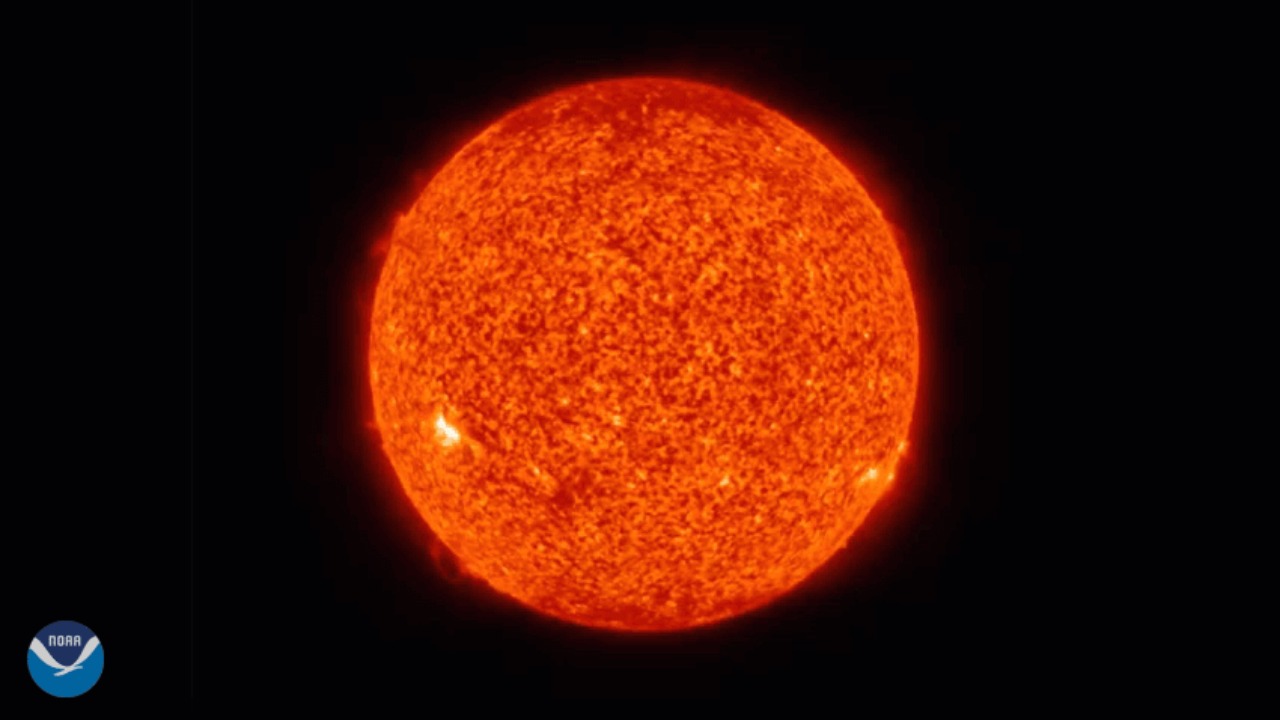

Solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are sudden eruptions of energy and particles from the sun’s surface. When these intense bursts of radiation reach Earth, they can disrupt our communication systems, satellites, and even power grids.
The potential for widespread damage is real, with the possibility of knocking out technology that modern society relies heavily on. A significant solar event could plunge entire regions into darkness, causing chaos and economic turmoil.
Accelerated Solar Wind
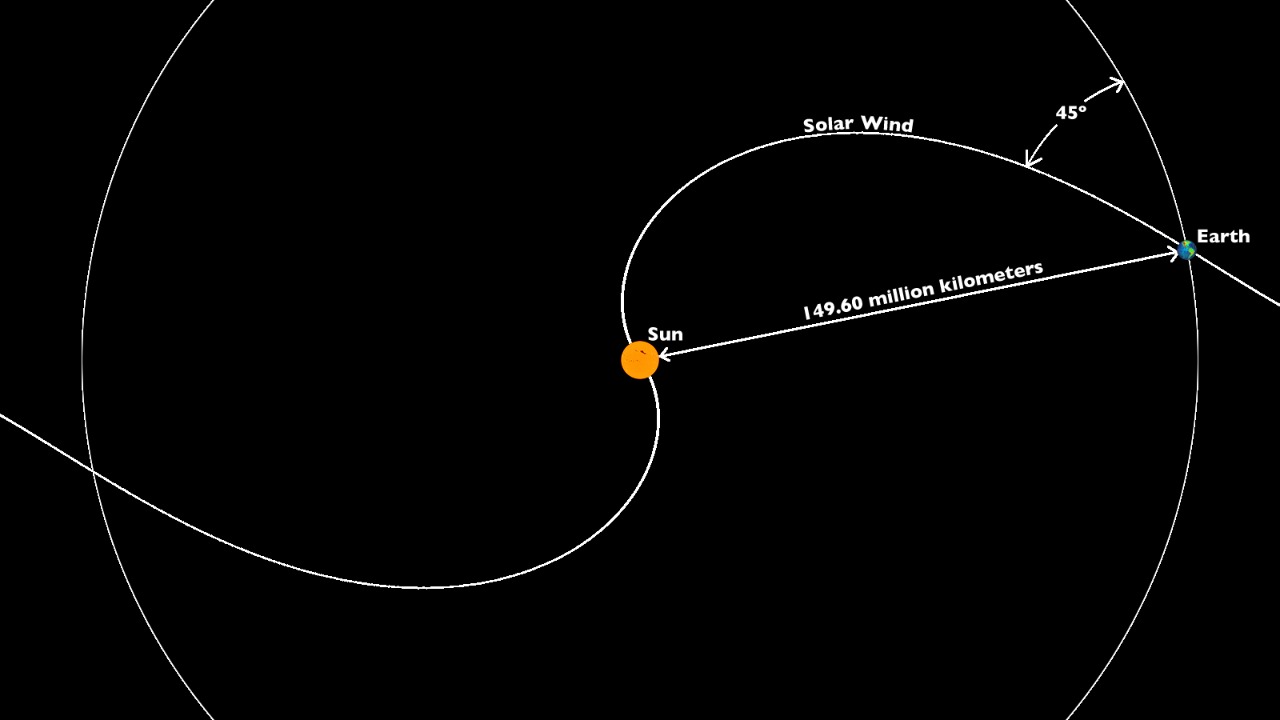
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles emitted by the sun, traveling through space at high speeds. An accelerated solar wind could pose a threat to Earth’s magnetic field, which shields us from harmful cosmic radiation.
If the solar wind’s intensity increases, it could weaken this protective barrier, leading to increased exposure to dangerous radiation levels. This could affect not only our technology but also human health, as higher radiation levels can increase cancer risks and other health issues.
Gradual Expansion into a Red Giant
In the distant future, the sun will gradually expand into a red giant, engulfing the inner planets, including Earth. Although this transformation is expected to occur billions of years from now, understanding this process helps us appreciate the sun’s lifecycle.
As the sun expands, it will lead to a significant increase in temperature on Earth, making it uninhabitable long before the sun consumes it. For more on the sun’s lifecycle, check out this comprehensive article.
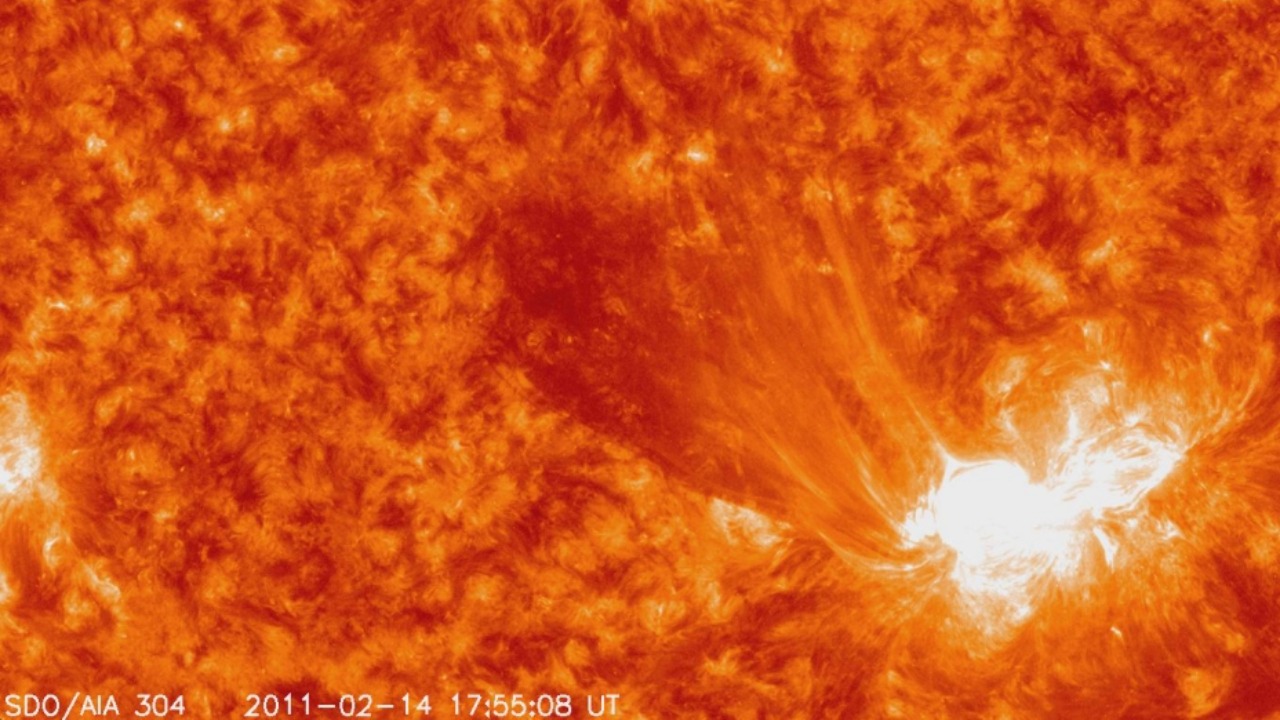
Orbital Instability Causing Earth to Spiral Inward
While less likely, a scenario involving orbital instability could cause Earth to spiral inward towards the sun. If the gravitational dynamics of our solar system were to change, possibly due to a passing celestial body, Earth’s orbit could become unstable.
This would result in a gradual decrease in the distance between Earth and the sun, eventually leading to our planet being incinerated. Although speculative, this theory highlights the delicate balance of celestial mechanics.
Multispectral Radiation Exposure
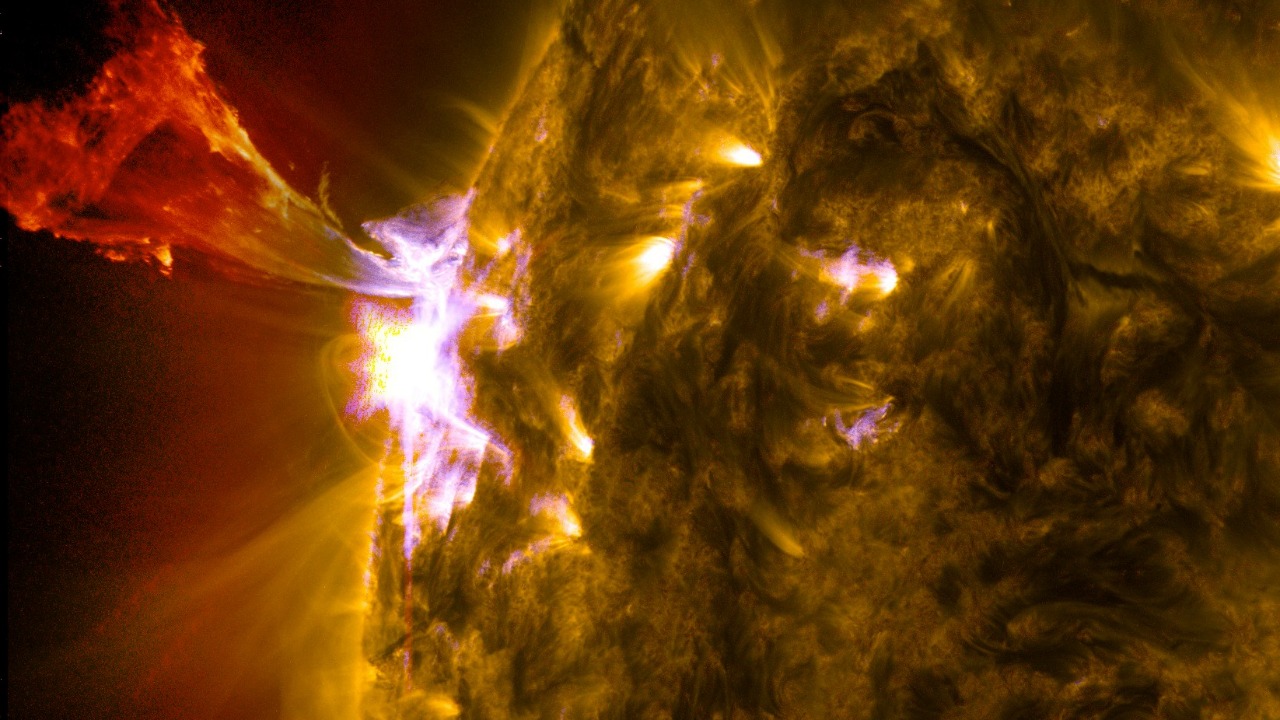

The sun emits radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum, from ultraviolet to X-rays. Multispectral radiation exposure could increase due to a thinning of Earth’s ozone layer or changes in the sun’s emission patterns.
This heightened exposure could lead to adverse effects on both ecosystems and human health, including increased rates of skin cancer and cataracts. Protecting our planet’s atmosphere is essential to mitigating these risks.
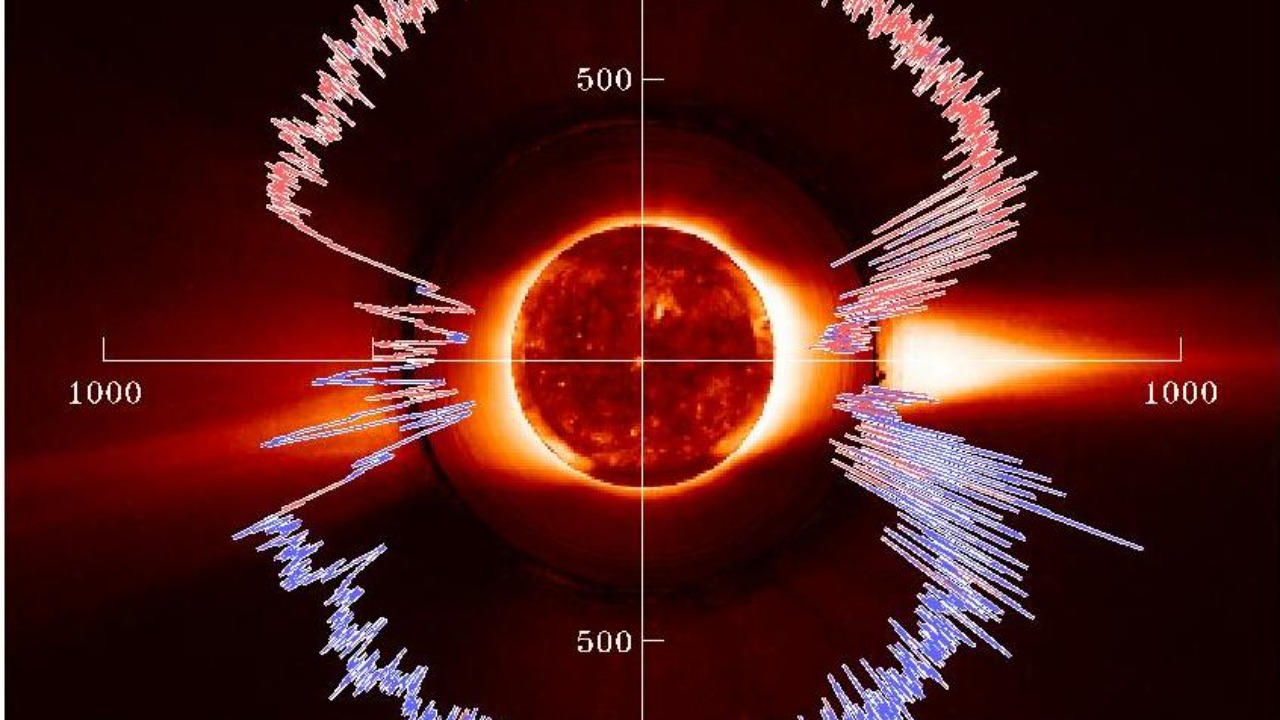
Intensified Solar Storms and Geomagnetic Disruptions
Solar storms are periods of intense solar activity that can disrupt Earth’s magnetosphere. These storms can cause geomagnetic disruptions, leading to widespread electrical outages and communication failures. As we approach solar maximum, the peak of the sun’s 11-year cycle, the risk of intensified solar storms increases.
Understanding and preparing for these disruptions is crucial to minimizing their impact on our technologically dependent world.