The pursuit of new energy sources is a critical endeavor in addressing the world’s growing energy needs. However, some promising technologies remain largely under the radar. Here are six emerging energy sources that are quietly making strides toward a more sustainable future.
Quantum Dot Solar Cells

Quantum dot solar cells represent an exciting advancement in photovoltaic technology. These cells utilize nanometer-sized semiconductor particles to significantly improve energy conversion efficiency. Due to their tunable properties, quantum dots can absorb a wider spectrum of sunlight compared to traditional solar cells. This innovation holds the potential for cheaper and more efficient solar panels, making solar energy more accessible to a broader audience.
Despite their potential, the widespread adoption of quantum dot solar cells has been slow. Challenges remain in terms of stability and scalability. However, ongoing research and development efforts are making strides in overcoming these hurdles, hinting at a promising future for this technology. For more information, check out this detailed study on quantum dot solar cells.
Biohybrid Solar Cells

Biohybrid solar cells are an innovative fusion of organic and inorganic materials. These cells leverage the natural photosynthetic processes of plants to capture and convert sunlight into energy. By incorporating biological molecules into their structure, biohybrid solar cells aim to achieve higher efficiency rates than conventional photovoltaic cells.
The potential applications for biohybrid solar cells are vast, ranging from self-sustaining buildings to portable charging solutions. While still in the experimental stages, this technology represents a groundbreaking approach to renewable energy. To delve deeper into biohybrid solar cells, explore this comprehensive overview.
Artificial Photosynthesis
Artificial photosynthesis seeks to replicate the natural process plants use to convert sunlight into chemical energy. By mimicking this process, scientists aim to produce renewable fuels like hydrogen and methanol directly from sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. This technology could play a crucial role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
While still in developmental phases, artificial photosynthesis has the potential to revolutionize how we generate and store energy. Research efforts continue to focus on improving the efficiency and scalability of these systems. For an update on the latest progress in this field, visit this informative resource.
Wave Energy Converters
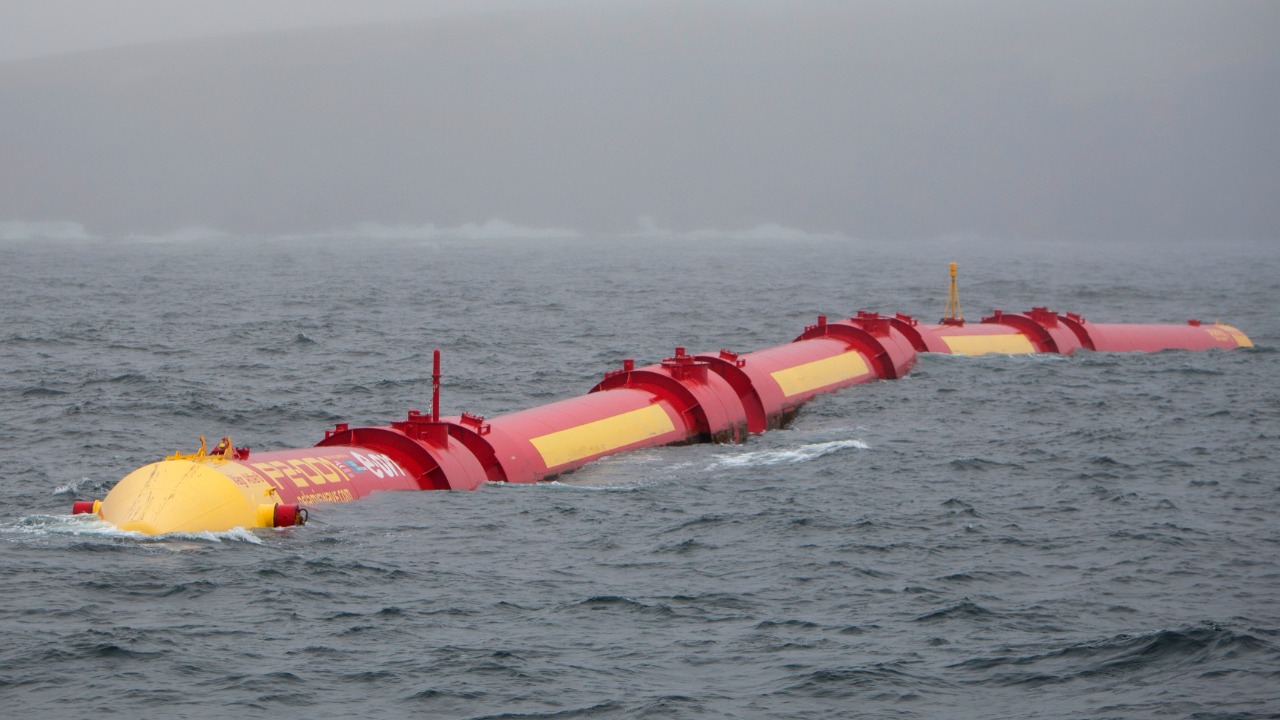

Wave energy converters harness the power of ocean waves to generate electricity. This form of renewable energy is particularly appealing due to the vast and untapped energy potential of the world’s oceans. Wave energy converters come in various designs, including point absorbers, oscillating water columns, and overtopping devices, each suited to different marine environments.
As a consistent and predictable energy source, wave energy could significantly contribute to global electricity supplies. However, technological and environmental challenges must be addressed to fully realize its potential. Further insights into wave energy can be explored through this link.
Algae Biofuel
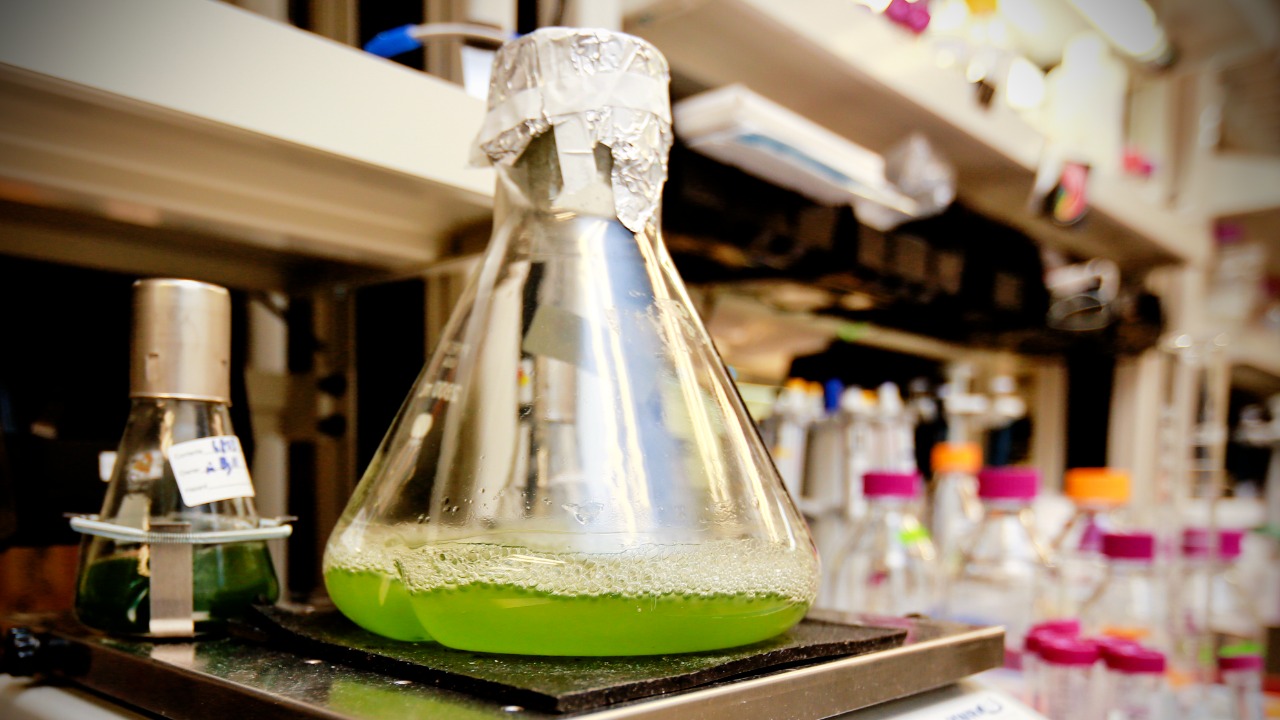

Algae biofuel is emerging as a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. Algae can be cultivated in a variety of environments and are capable of producing high yields of oil, which can be refined into biodiesel. This renewable energy source offers a sustainable solution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and lessening our dependence on oil.
Despite its promise, the commercialization of algae biofuel faces challenges related to cost and scalability. However, ongoing research is focused on improving production methods and reducing costs. For a glimpse into how algae biofuel is shaping the future of energy, visit this resource.
Thorium Reactors
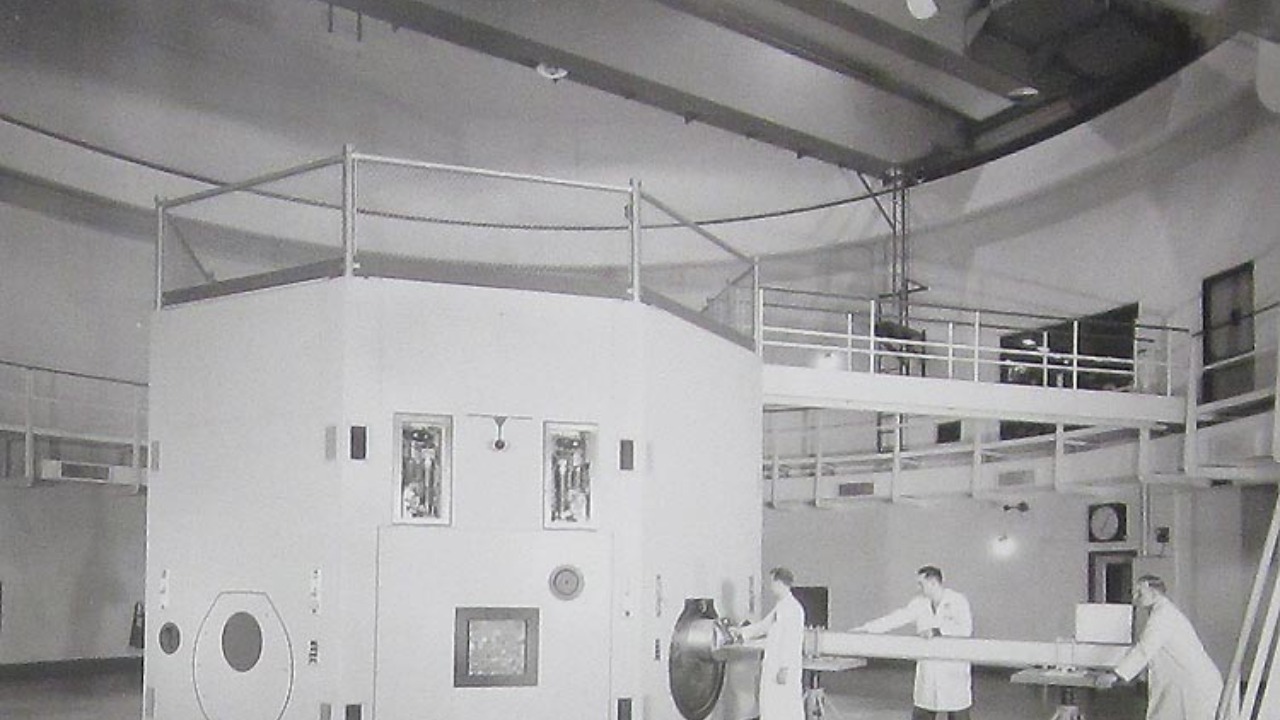

Thorium reactors offer a safer and more abundant alternative to traditional nuclear reactors. Thorium is a naturally occurring element that is more plentiful than uranium and has the potential to generate nuclear power with less waste and reduced risk of meltdown. These reactors also produce less long-lived radioactive waste, addressing one of the major drawbacks of conventional nuclear power.
The development of thorium reactors has been largely overshadowed by other nuclear technologies, but interest in this energy source is growing. With advances in reactor design and safety, thorium could become a key player in the global energy landscape. To learn more about the potential of thorium reactors, explore this resource.