Throughout history, certain gadgets have not only transformed the way we live but have also significantly influenced the course of human development. From ancient inventions that laid the groundwork for modern society to recent technological breakthroughs that continue to shape our future, these gadgets have left an indelible mark on the world. Here, we explore 13 such gadgets that have changed history, drawing on authoritative sources to highlight their impact.
The Wheel
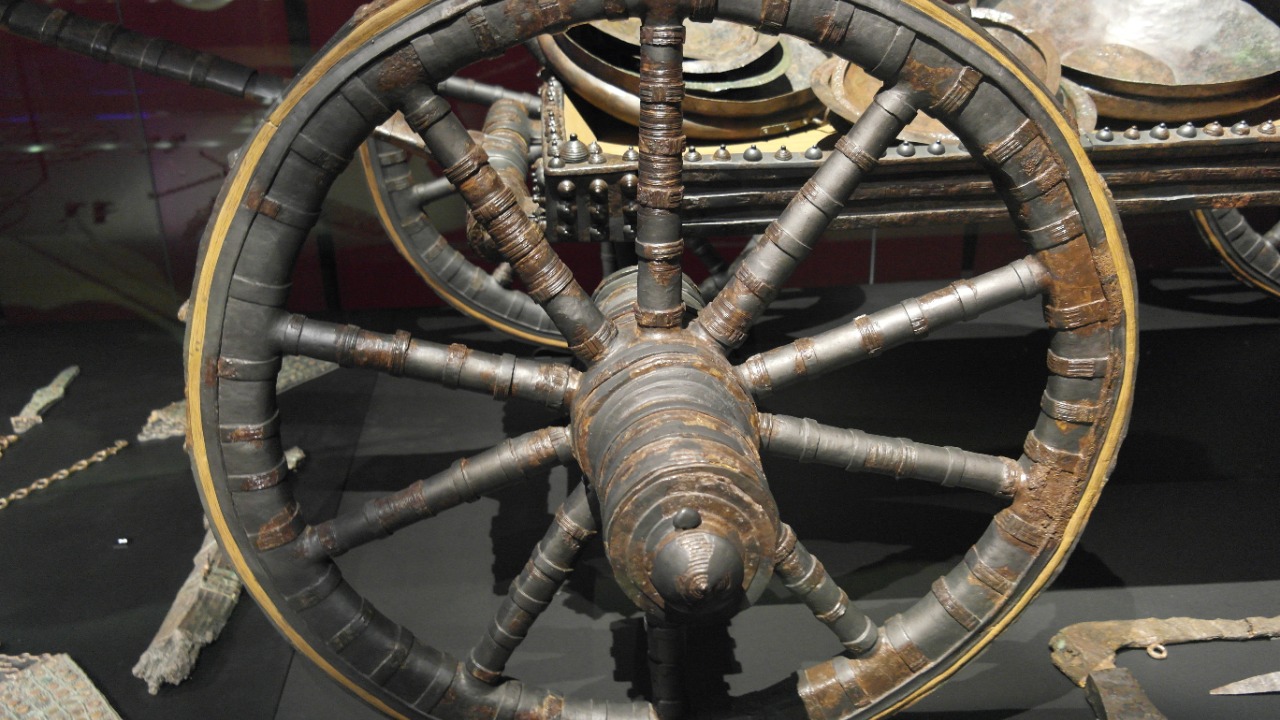

The wheel is often hailed as one of the most foundational inventions in human history. Its development revolutionized transportation and enabled the movement of goods and people over long distances, laying the groundwork for trade and cultural exchange. According to National Geographic, the wheel’s invention was a pivotal moment that facilitated the growth of civilizations by enhancing mobility and efficiency.
Beyond transportation, the wheel’s influence extended to various industries, including agriculture and manufacturing. It enabled the creation of complex machinery and tools, which in turn increased productivity and innovation. The wheel’s simplicity belies its profound impact, making it a cornerstone of technological advancement.
The wheel’s invention is believed to have occurred around 3500 B.C. in Mesopotamia, where it was initially used for pottery making. Its application in transportation came later, revolutionizing how societies moved goods and people. The wheel’s design evolved over time, leading to innovations such as the spoked wheel, which reduced weight and improved efficiency. This evolution was crucial in the development of chariots and later vehicles, which played significant roles in warfare and trade. The wheel’s adaptability and utility have made it a timeless invention, influencing countless technologies and industries throughout history.
The Compass
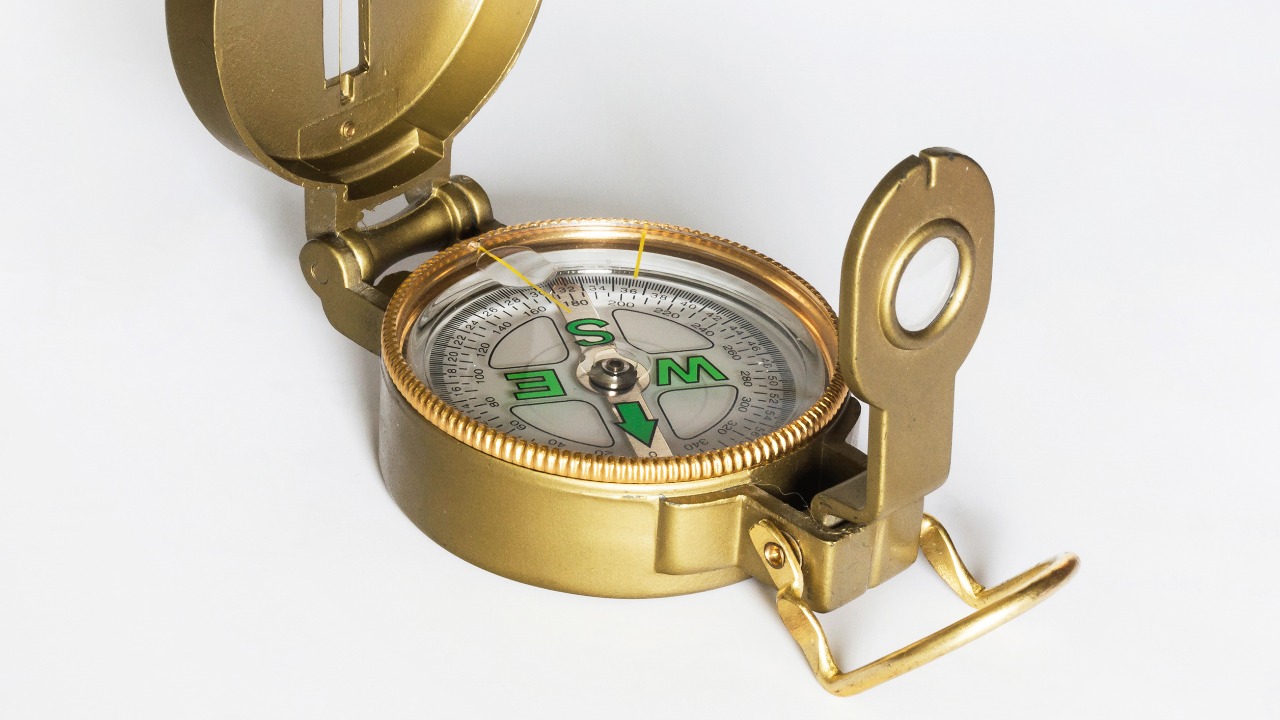

The compass, a navigational breakthrough, transformed exploration by allowing sailors to determine direction accurately, even when landmarks were not visible. This invention was crucial for the age of exploration, enabling voyages across uncharted waters and the discovery of new lands. As highlighted by National Geographic, the compass played a vital role in expanding trade routes and cultural interactions.
Its impact on navigation cannot be overstated, as it provided explorers with the confidence to venture further than ever before. The compass’s ability to guide travelers through unknown territories made it an indispensable tool for maritime exploration and contributed significantly to the globalization of the world.
Originating in China during the Han Dynasty, the compass was initially used for divination before its navigational potential was realized. By the 11th century, it had become an essential tool for maritime navigation, allowing sailors to venture into open seas with greater confidence. The compass’s ability to provide a reliable sense of direction was instrumental in the Age of Discovery, facilitating the European exploration of the Americas and other distant lands. This not only expanded geographical knowledge but also led to the establishment of new trade routes and the exchange of goods and ideas on a global scale.
The Printing Press
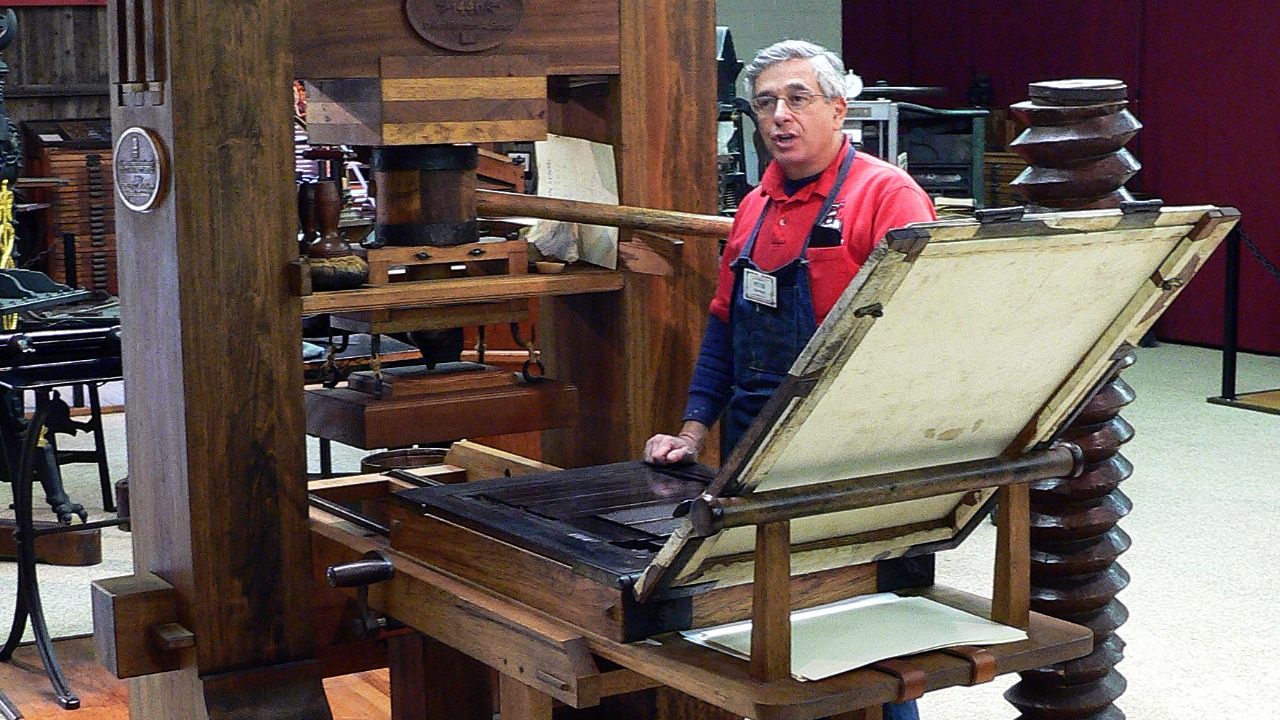

The printing press, invented by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century, revolutionized the dissemination of knowledge. By making books more accessible and affordable, it sparked an information age that transformed education and literacy. According to Live Science, the printing press is considered one of the top inventions that changed the world by democratizing knowledge.
This invention facilitated the spread of ideas and played a crucial role in major historical movements, such as the Renaissance and the Reformation. The ability to mass-produce written material allowed for the rapid exchange of information, fostering intellectual growth and cultural development across Europe and beyond.
Gutenberg’s printing press utilized movable type, a revolutionary concept that drastically reduced the time and cost of producing books. This innovation democratized access to information, previously restricted to the elite, and fueled the spread of literacy. The printing press played a pivotal role in the Protestant Reformation by enabling the rapid dissemination of Martin Luther’s theses and other reformist writings. It also contributed to the Scientific Revolution by allowing scientists to share their discoveries widely, thus accelerating the advancement of knowledge and laying the groundwork for modern science.
The Steam Engine
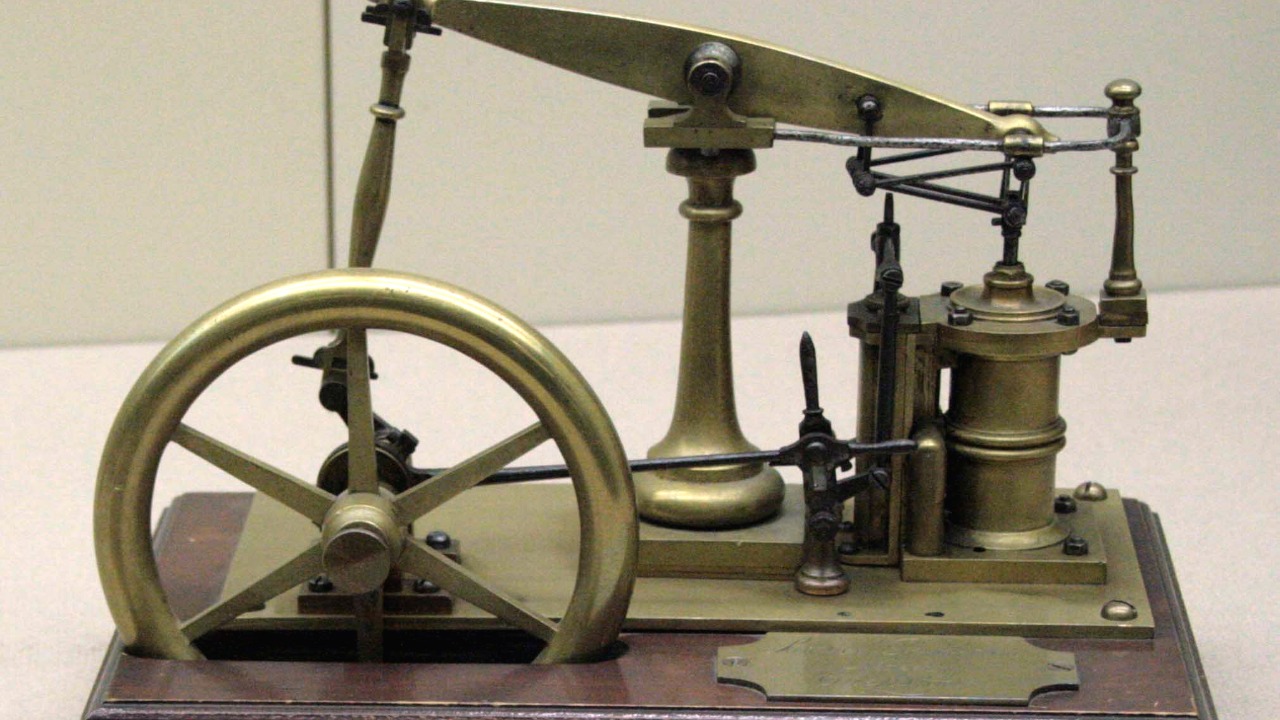
The steam engine was a driving force behind the Industrial Revolution, powering factories, trains, and ships. Its invention marked a significant shift from manual labor to mechanized production, leading to unprecedented economic growth and urbanization. As noted by Live Science, the steam engine is among the top inventions that reshaped the world by enabling industrialization.
By providing a reliable and efficient source of power, the steam engine facilitated the mass production of goods and the expansion of industries. It also revolutionized transportation, reducing travel time and costs, and played a crucial role in the development of modern infrastructure.
The steam engine’s development by James Watt in the 18th century marked a turning point in industrialization. Watt’s improvements, including the separate condenser, significantly increased efficiency and power output, making steam engines viable for a wide range of applications. This innovation powered the mechanization of industries such as textiles and mining, leading to increased production and economic growth. The steam engine also revolutionized transportation, with steam-powered locomotives and ships reducing travel time and costs, thus facilitating the movement of goods and people and contributing to the expansion of global trade networks.
The Telegraph

The telegraph was a pioneering communication device that transformed global connectivity by enabling instant long-distance communication. This invention laid the groundwork for the modern telecommunications industry and accelerated the pace of information exchange. According to CNET, the telegraph is one of the 25 technologies that changed the world by bridging vast distances.
Its impact was felt across various sectors, including commerce, journalism, and diplomacy, as it allowed for real-time communication and coordination. The telegraph’s ability to transmit messages quickly and reliably revolutionized the way people interacted and conducted business, paving the way for future innovations in communication technology.
Invented by Samuel Morse in the 1830s, the telegraph system used electrical signals to transmit messages over long distances via wires. This breakthrough in communication technology allowed for the rapid exchange of information, which was crucial for businesses, governments, and the military. The telegraph played a significant role during the American Civil War, enabling real-time communication between distant locations. It also laid the foundation for future innovations in telecommunications, such as the telephone and the internet, by demonstrating the potential of electronic communication to connect people across vast distances.
The Light Bulb

The invention of the light bulb by Thomas Edison illuminated modern life, extending productive hours beyond daylight and transforming urban environments. This electrical gadget, as highlighted by CNET, is among the 25 technologies that have changed the world by making artificial lighting accessible to the masses.
The light bulb’s impact on society was profound, as it improved safety, enhanced quality of life, and enabled new forms of entertainment and industry. By providing a reliable and efficient source of light, it facilitated the growth of cities and contributed to the development of modern infrastructure.
Edison’s development of the practical incandescent light bulb in 1879 was a culmination of efforts by various inventors. His version, which used a carbon filament, was both long-lasting and commercially viable. The widespread adoption of electric lighting transformed urban life, extending work and leisure hours and improving safety in public spaces. The light bulb’s impact extended beyond illumination; it spurred the growth of the electrical industry, leading to the development of power grids and the electrification of homes and businesses, which in turn drove further technological advancements and economic growth.
The Personal Computer

The personal computer revolutionized daily productivity by bringing computing power into homes and offices. This transformative gadget, as cited by Reader’s Digest, is one of the 19 inventions that have changed the world in the last decade by reshaping how we work, learn, and communicate.
Personal computers have enabled the digital age, providing access to information, tools for creativity, and platforms for social interaction. Their versatility and accessibility have made them indispensable in various fields, from education and business to entertainment and research, driving innovation and connectivity worldwide.
The personal computer emerged in the 1970s and 1980s, with companies like Apple and IBM leading the charge. These devices brought computing power to individuals and small businesses, transforming how work was performed and information was processed. The personal computer facilitated the rise of software industries, including word processing, spreadsheets, and graphic design, which revolutionized various professional fields. Additionally, PCs played a crucial role in the development of the internet, providing the hardware necessary for individuals to access and contribute to the burgeoning digital world, thus accelerating the pace of technological and social change.
The Internet

The internet is a networking revolution that has transformed every aspect of modern life, from communication and commerce to education and entertainment. As described by Reader’s Digest, the internet is among the 19 inventions from the last decade that have reshaped the world by connecting people and information globally.
Its impact is unparalleled, as it has created new industries, facilitated the exchange of ideas, and democratized access to information. The internet’s ability to connect billions of people and devices has revolutionized how we interact, work, and live, making it one of the most significant inventions in human history.
The internet’s origins can be traced back to ARPANET, a project funded by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1960s. It evolved into a global network of interconnected computers, enabling unprecedented levels of communication and information sharing. The development of the World Wide Web in the 1990s by Tim Berners-Lee further expanded the internet’s capabilities, making it accessible to the general public. This connectivity has transformed industries, from media and entertainment to education and healthcare, by providing platforms for innovation, collaboration, and the democratization of information on a global scale.
The Airplane

The airplane, an aviation milestone, contracted global distances by enabling rapid travel across continents. This invention, as positioned by National Geographic, is one of the 10 inventions that changed the world by making international travel accessible and efficient.
Airplanes have revolutionized transportation, facilitating global trade, tourism, and cultural exchange. Their ability to transport people and goods quickly and safely has transformed economies and societies, making the world more interconnected and accessible than ever before.
The Wright brothers’ successful flight in 1903 marked the beginning of the aviation era. Airplanes quickly evolved from experimental machines to essential tools for transportation and warfare. During World War I and II, aircraft played crucial roles in reconnaissance and combat, demonstrating their strategic importance. In peacetime, commercial aviation expanded rapidly, shrinking the world by making distant locations accessible within hours. This revolution in transportation has facilitated global trade, tourism, and cultural exchange, contributing to the economic and social interconnectedness of the modern world.
The Transistor
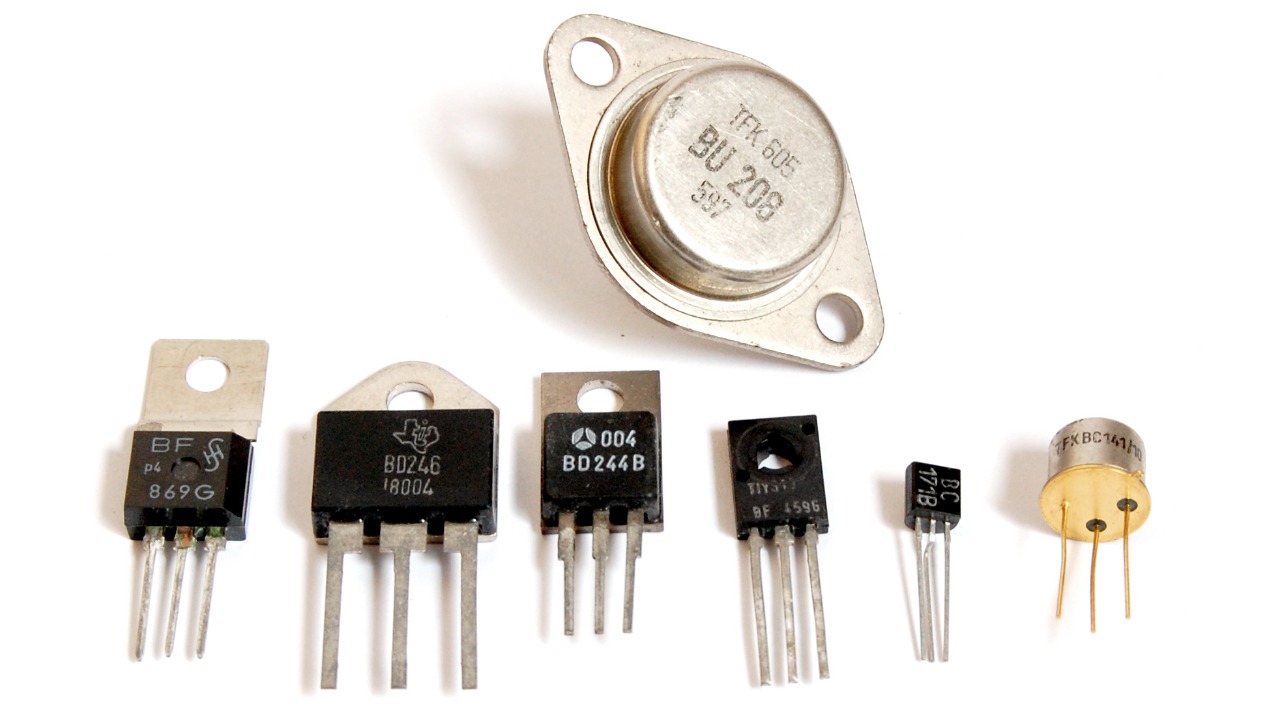
The transistor, a semiconductor gadget, is acknowledged for enabling the development of modern electronics. As highlighted by Live Science, the transistor is among the top 10 inventions that changed the world by powering everything from computers to smartphones.
Its invention marked a significant advancement in technology, allowing for the miniaturization and increased efficiency of electronic devices. The transistor’s impact on the electronics industry has been profound, leading to the development of integrated circuits and the digital revolution.
Invented in 1947 by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, the transistor replaced vacuum tubes in electronic devices, offering a smaller, more reliable, and energy-efficient alternative. This breakthrough enabled the miniaturization of electronic circuits, leading to the development of modern computers, smartphones, and countless other devices. The transistor’s impact on technology is profound, as it laid the foundation for the digital age, driving advancements in computing power and enabling the creation of complex integrated circuits that power today’s electronic world.
The Smartphone

The smartphone, a mobile integration gadget, has transformed how we communicate, access information, and interact with the world. As encompassed by CNET, the smartphone is one of the 25 technologies that have changed the world by integrating multiple functions into a single device.
Smartphones have become essential tools for daily life, offering connectivity, entertainment, and productivity at our fingertips. Their impact on society is immense, as they have changed how we work, socialize, and consume media, making them a cornerstone of modern technology.
Since the introduction of the first iPhone in 2007, smartphones have rapidly evolved, integrating features such as high-resolution cameras, GPS, and internet connectivity. These devices have transformed communication by enabling instant access to information and social networks. Smartphones have also revolutionized industries such as photography, navigation, and entertainment, providing tools for creativity and productivity in a compact form. Their widespread adoption has reshaped societal norms and behaviors, influencing how we interact, work, and consume media, making them indispensable in modern life.
GPS
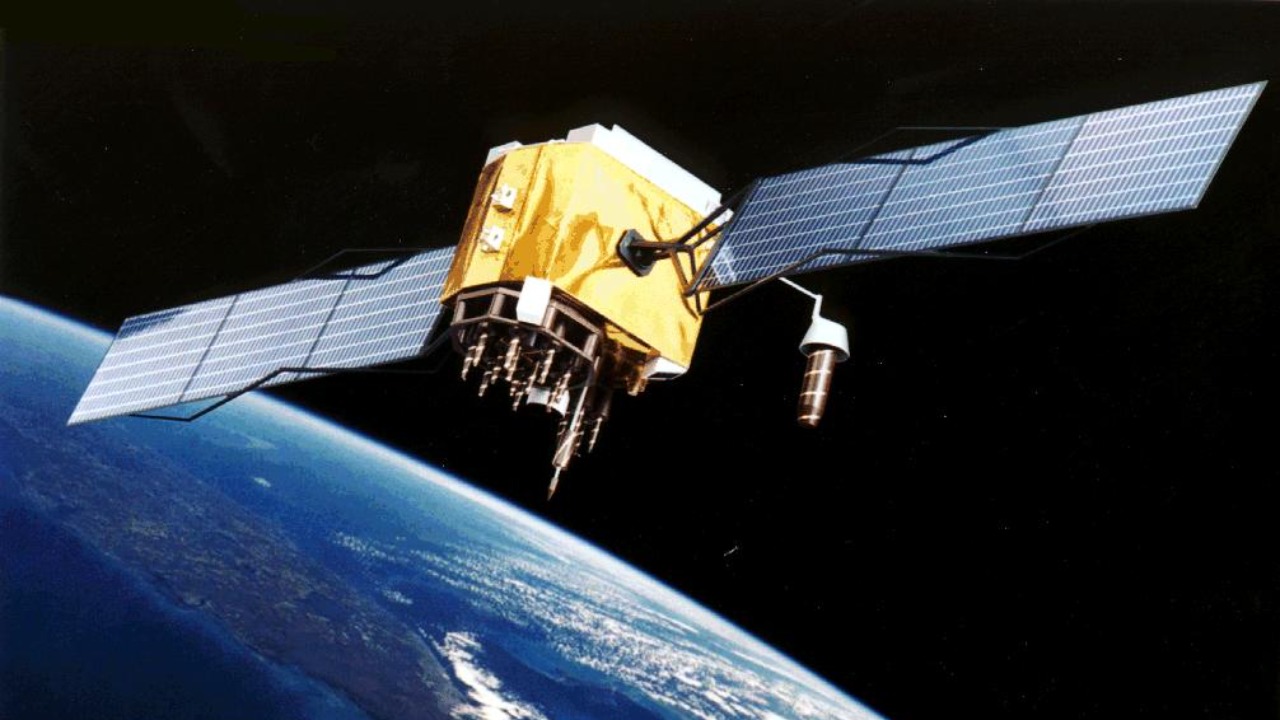

GPS, a location innovation, has revolutionized navigation by providing precise positioning and timing information. As presented by Reader’s Digest, GPS is among the 19 inventions that have changed the world in the last decade by enhancing navigation and location-based services.
Its applications are vast, ranging from personal navigation and logistics to scientific research and emergency response. GPS technology has improved safety, efficiency, and convenience in various fields, making it an indispensable tool in the modern world.
Developed by the U.S. Department of Defense, the Global Positioning System (GPS) became fully operational in the 1990s, providing accurate location and timing information worldwide. This technology has revolutionized navigation, making it possible to pinpoint precise locations anywhere on Earth. GPS is used in various applications, from guiding vehicles and aircraft to tracking wildlife and monitoring environmental changes. Its impact extends to everyday life, enhancing personal navigation and enabling location-based services that improve convenience and efficiency in numerous sectors, including transportation, logistics, and emergency response.
The Transistor Radio
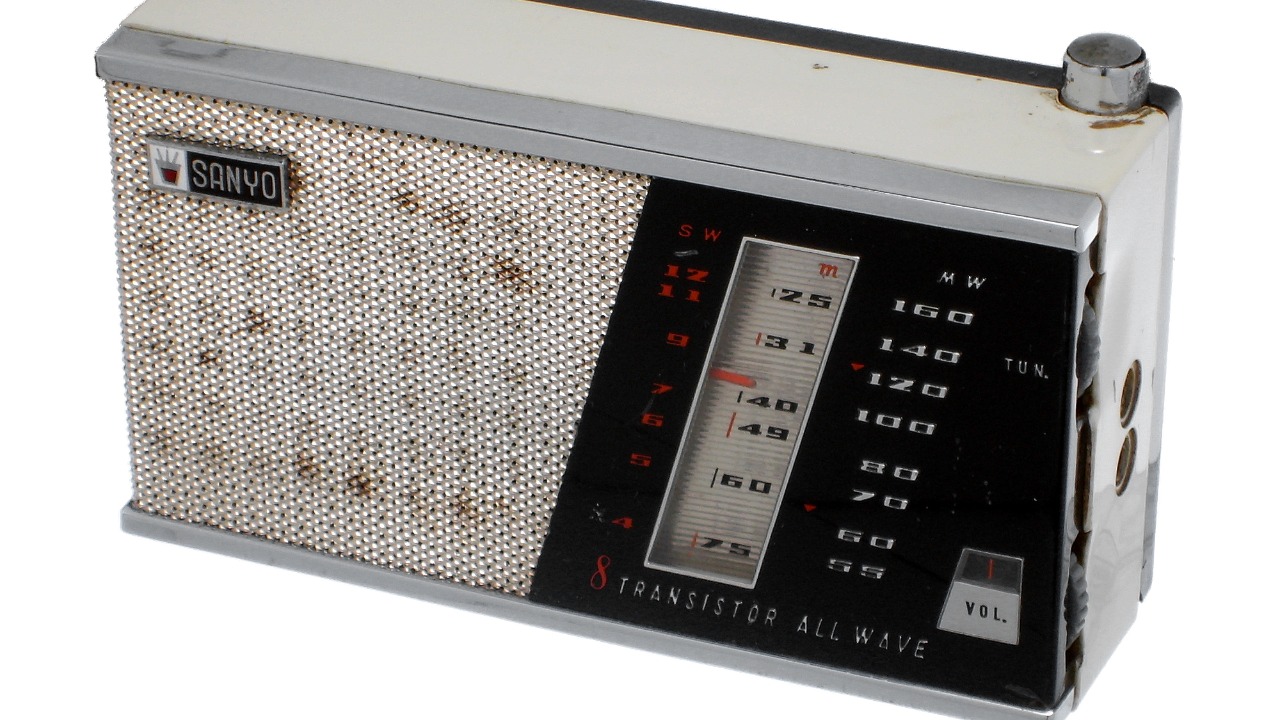

The transistor radio, linked to cultural explosions in pivotal years like 1956 and 1966, played a significant role in shaping modern culture. As reviewed in The Guardian, this gadget was instrumental in spreading music and information, influencing social and cultural movements.
By making radio broadcasts portable and accessible, the transistor radio democratized access to information and entertainment. It became a symbol of youth culture and rebellion, contributing to the cultural revolutions of the mid-20th century and leaving a lasting impact on society.
The transistor radio, introduced in the 1950s, was a groundbreaking development in portable electronics. It allowed people to listen to music and news on the go, fostering a sense of connection and community. This portability contributed to the rise of popular music and the spread of cultural movements, as people could easily access broadcasts from different regions. The transistor radio also played a role in political and social change, as it provided a platform for disseminating information and ideas, influencing public opinion and contributing to the cultural revolutions of the 20th century.